-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Biჼ MASK i₽ 0 _ 255
As a developer or network engineer, you may need to occasionally look up subnet mask values and figure out what they mean.
To make your life easier, the freeCodeCamp community has made this simple cheat sheet. Just scroll or use Ctrl/Cmd + f to find the value you're looking for.
Here are the charts, followed by some explanations of what they mean.
CIDR | SUBNET MASK | WILDCARD MASK | # OF IP ADDRESSES | # OF USABLE IP ADDRESSES -- | -- | -- | -- | -- /32 | 255.255.255.255 | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 1 /31 | 255.255.255.254 | 0.0.0.1 | 2 | 2* /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 0.0.0.3 | 4 | 2 /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 0.0.0.7 | 8 | 6 /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 0.0.0.15 | 16 | 14 /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 0.0.0.31 | 32 | 30 /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 0.0.0.63 | 64 | 62 /25 | 255.255.255.128 | 0.0.0.127 | 128 | 126 /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 0.0.0.255 | 256 | 254 /23 | 255.255.254.0 | 0.0.1.255 | 512 | 510 /22 | 255.255.252.0 | 0.0.3.255 | 1,024 | 1,022 /21 | 255.255.248.0 | 0.0.7.255 | 2,048 | 2,046 /20 | 255.255.240.0 | 0.0.15.255 | 4,096 | 4,094 /19 | 255.255.224.0 | 0.0.31.255 | 8,192 | 8,190 /18 | 255.255.192.0 | 0.0.63.255 | 16,384 | 16,382 /17 | 255.255.128.0 | 0.0.127.255 | 32,768 | 32,766 /16 | 255.255.0.0 | 0.0.255.255 | 65,536 | 65,534 /15 | 255.254.0.0 | 0.1.255.255 | 131,072 | 131,070 /14 | 255.252.0.0 | 0.3.255.255 | 262,144 | 262,142 /13 | 255.248.0.0 | 0.7.255.255 | 524,288 | 524,286 /12 | 255.240.0.0 | 0.15.255.255 | 1,048,576 | 1,048,574 /11 | 255.224.0.0 | 0.31.255.255 | 2,097,152 | 2,097,150 /10 | 255.192.0.0 | 0.63.255.255 | 4,194,304 | 4,194,302 /9 | 255.128.0.0 | 0.127.255.255 | 8,388,608 | 8,388,606 /8 | 255.0.0.0 | 0.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 | 16,777,214 /7 | 254.0.0.0 | 1.255.255.255 | 33,554,432 | 33,554,430 /6 | 252.0.0.0 | 3.255.255.255 | 67,108,864 | 67,108,862 /5 | 248.0.0.0 | 7.255.255.255 | 134,217,728 | 134,217,726 /4 | 240.0.0.0 | 15.255.255.255 | 268,435,456 | 268,435,454 /3 | 224.0.0.0 | 31.255.255.255 | 536,870,912 | 536,870,910 /2 | 192.0.0.0 | 63.255.255.255 | 1,073,741,824 | 1,073,741,822 /1 | 128.0.0.0 | 127.255.255.255 | 2,147,483,648 | 2,147,483,646 /0 | 0.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.255 | 4,294,967,296 | 4,294,967,294In this case, because all the bits for this octet in the subnet mask are "off", we can be certain that all of the corresponding bits for this octet in the IP address are part of the host.
When you write CIDR notation it's usually done with the network ID. So the CIDR notation of the IP address 192.168.0.101 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 is 192.168.0.0/24.
To see more examples of how to calculate the CIDR notation and network ID for a given IP address and subnet mask, check out this video:
Now that we've gone over some basic examples of subnetting and CIDR, let's zoom out and look at what's known as Classful IP addressing.
Back before subnetting was developed, all IP addresses fell into a particular class:
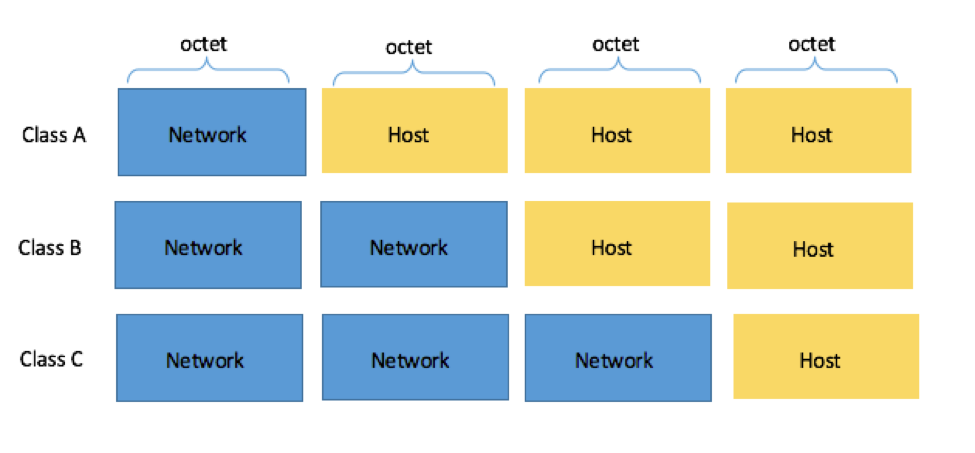 Source: Subnetting for dummies
Source: Subnetting for dummiesNote that there are class D and E IP addresses, but we'll go into these in more detail a bit later.
Classful IP addresses gave network engineers a way to provide different organizations with a range of valid IP addresses.
There were a lot of issues with this approach that eventually lead to subnetting. But before we get into those, let's take a closer look at the different classes.
For Class A IP addresses, the first octet (8 bits / 1 byte) represent the network ID, and the remaining three octets (24 bits / 3 bytes) are the host ID.
Class A IP addresses range from 1.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255, with a default mask of 255.0.0.0 (or /8 in CIDR).
This means that Class A addressing can have a total of 128 (27) networks and 16,777,214 (224-2) usable addresses per network.
Also, note that the range 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 within the Class A range is reserved for host loopback address (see RFC5735).
For Class B IP addresses, the first two octets (16 bits / 2 bytes) represent the network ID and the remaining two octets (16 bits / 2 bytes) are the host ID.
Class B IP addresses range from 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255, with a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 (or /16 in CIDR).
Class B addressing can have 16,384 (214) network addresses and 65,534 (216) usable addresses per network.
For Class C IP addresses, the first three octets (24 bits / 3 bytes) represent the network ID and the last octet (8 bits / 1 bytes) is the host ID.
Class C IP Addresses range from 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255, with a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (or /24 in CIDR).
Class C translates to 2,097,152 (221) networks and 254 (28-2) usable addresses per network.
The last two classes are Class D and Class E.
Class D IP addresses are reserved for multicasts. They occupy the range from 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
Class E IP addresses are experimental, and are anything over 240.0.0.0.
The main issue with classful IP addresses is that it wasn't efficient, and could lead to a lot of wasted IP addresses.
For example, imagine that you're part of a large organization back then. Your company has 1,000 employees, meaning that it would fall into class B.
But if you look above, you'll see that a class B network can support up to 65,534 usable addresses. That's way more than your organization would likely need, even if each employee had multiple devices with a unique address.
And there was no way your organization could fall back to class C – there just wouldn't be enough usable IP addresses.
So while classful IP addresses were used around the time IPv4 addresses became widespread, it quickly became clear that a better system would be necessary to ensure we wouldn't use up all of the ~4.2 billion usable addresses.
Classful IP addresses haven't been used since they were replaced by CIDR in 1993, and are mostly studied to understand early internet architecture, and why subnetting is important.
To make your life easier, the freeCodeCamp community has made this simple cheat sheet. Just scroll or use Ctrl/Cmd + f to find the value you're looking for.
Here are the charts, followed by some explanations of what they mean.
CIDR SUBNET MASK WILDCARD MASK # OF IP ADDRESSES # OF USABLE IP ADDRESSES /32 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0 1 1 /31 255.255.255.254 0.0.0.1 2 2* /30 255.255.255.252 0.0.0.3 4 2 /29 255.255.255.248 0.0.0.7 8 6 /28 255.255.255.240 0.0.0.15 16 14 /27 255.255.255.224 0.0.0.31 32 30 /26 255.255.255.192 0.0.0.63 64 62 /25 255.255.255.128 0.0.0.127 128 126 /24 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.255 256 254 /23 255.255.254.0 0.0.1.255 512 510 /22 255.255.252.0 0.0.3.255 1,024 1,022 /21 255.255.248.0 0.0.7.255 2,048 2,046 /20 255.255.240.0 0.0.15.255 4,096 4,094 /19 255.255.224.0 0.0.31.255 8,192 8,190 /18 255.255.192.0 0.0.63.255 16,384 16,382 /17 255.255.128.0 0.0.127.255 32,768 32,766 /16 255.255.0.0 0.0.255.255 65,536 65,534 /15 255.254.0.0 0.1.255.255 131,072 131,070 /14 255.252.0.0 0.3.255.255 262,144 262,142 /13 255.248.0.0 0.7.255.255 524,288 524,286 /12 255.240.0.0 0.15.255.255 1,048,576 1,048,574 /11 255.224.0.0 0.31.255.255 2,097,152 2,097,150 /10 255.192.0.0 0.63.255.255 4,194,304 4,194,302 /9 255.128.0.0 0.127.255.255 8,388,608 8,388,606 /8 255.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 16,777,216 16,777,214 /7 254.0.0.0 1.255.255.255 33,554,432 33,554,430 /6 252.0.0.0 3.255.255.255 67,108,864 67,108,862 /5 248.0.0.0 7.255.255.255 134,217,728 134,217,726 /4 240.0.0.0 15.255.255.255 268,435,456 268,435,454 /3 224.0.0.0 31.255.255.255 536,870,912 536,870,910 /2 192.0.0.0 63.255.255.255 1,073,741,824 1,073,741,822 /1 128.0.0.0 127.255.255.255 2,147,483,648 2,147,483,646 /0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 4,294,967,296 4,294,967,294
- /31 is a special case detailed in RFC 3021 where networks with this type of subnet mask can assign two IP addresses as a point-to-point link.
And here's a table of the decimal to binary conversions for subnet mask and wildcard octets:
SUBNET MASK WILDCARD 0 00000000 255 11111111 128 10000000 127 01111111 192 11000000 63 00111111 224 11100000 31 00011111 240 11110000 15 00001111 248 11111000 7 00000111 252 11111100 3 00000011 254 11111110 1 00000001 255 11111111 0 00000000 Note that the wildcard is just the inverse of the subnet mask.
If you are new to network engineering, you can get a better idea of how computer networks work here.
Finally, this cheat sheet and the rest of the article is focused on IPv4 addresses, not the newer IPv6 protocol. If you'd like to learn more about IPv6, check out the article on computer networks above.
How Do IP Address Blocks Work? IPv4 addresses like 192.168.0.1 are really just decimal representations of four binary blocks.
Each block is 8 bits, and represents numbers from 0-255. Because the blocks are groups of 8 bits, each block is known as an octet. And since there are four blocks of 8 bits, every IPv4 address is 32 bits.
For example, here's what the IP address 172.16.254.1 looks like in binary:
1125px-Ipv4_address Source: IPv4 To convert an IP address between its decimal and binary forms, you can use this chart:
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 x x x x x x x x The chart above represents one 8 bit octive.
Now lets say you want to convert the IP address 168.210.225.206. All you need to do is break the address into four blocks (168, 210, 225, and 206), and convert each into binary using the chart above.
Remember that in binary, 1 is the equivalent to "on" and 0 is "off". So to convert the first block, 168, into binary, just start from the beginning of the chart and place a 1 or 0 in that cell until you get a sum of 168.
For example:
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 128 + 32 + 8 = 168, which in binary is 10101000.
If you do this for the rest of the blocks, you'd get 10101000.11010010.11100001.11001110.
What is Subnetting? If you look at the table above, it can seem like the number of IP addresses is practically unlimited. After all, there are almost 4.2 billion possible IPv4 addresses available.
But if you think about how much the internet has grown, and how many more devices are connected these days, it might not surprise you to hear that there's already a shortage of IPv4 addresses.
Because the shortage was recognized years ago, developers came up with a way to split up an IP address into smaller networks called subnets.
This process, called subnetting, uses the host section of the IP address to break it down into those smaller networks or subnets.
Generally, an IP address is made up of network bits and host bits:
network-and-host-bits Source: What is IPv4 So generally, subnetting does two things: it gives us a way to break up networks into subnets, and allows devices to determine whether another device/IP address is on the same local network or not.
A good way to think about subnetting is to picture your wireless network at home.
Without subnetting, every internet connected device would need its own unique IP address.
But since you have a wireless router, you just need one IP address for your router. This public or external IP address is usually handled automatically, and is assigned by your internet service provider (ISP).
Then every device connected to that router has its own private or internal IP address:
home-network-diagram Source: What Is My IP Address? Now if your device with the internal IP address 192.168.1.101 wants to communicate with another device, it'll use the IP address of the other device and the subnet mask.
The combination of the IP addresses and subnet mask allows the device at 192.168.1.101 to figure out if the other device is on the same network (like the device at 192.168.1.103), or on a completely different network somewhere else online.
Interestingly, the external IP address assigned to your router by your ISP is probably part of a subnet, which might include many other IP addresses for nearby homes or businesses. And just like internal IP addresses, it also needs a subnet mask to work.
How Subnet Masks Work Subnet masks function as a sort of filter for an IP address. With a subnet mask, devices can look at an IP address, and figure out which parts are the network bits and which are the host bits.
Then using those things, it can figure out the best way for those devices to communicate.
If you've poked around the network settings on your router or computer, you've likely seen this number: 255.255.255.0.
If so, you've seen a very common subnet mask for simple home networks.
Like IPv4 addresses, subnet masks are 32 bits. And just like converting an IP address into binary, you can do the same thing with a subnet mask.
For example, here's our chart from earlier:
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 x x x x x x x x Now let's convert the first octet, 255:
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Pretty simple, right? So any octet that's 255 is just 11111111 in binary. This means that 255.255.255.0 is really 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 in binary.
Now let's look at a subnet mask and IP address together and calculate which parts of the IP address are the network bits and host bits.
Here are the two in both decimal and binary:
TYPE DECIMAL BINARY IP address 192.168.0.101 11000000.10101000.00000000.01100101 Subnet mask 255.255.255.0 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 With the two laid out like this, it's easy to separate 192.168.0.101 into network bits and host bits.
Whenever a bit in a binary subnet mask is 1, then the same bit in a binary IP address is part of the network, not the host.
Since the octet 255 is 11111111 in binary, that whole octet in the IP address is part of the network. So the first three octets, 192.168.0, is the network portion of the IP address, and 101 is the host portion.
In other words, if the device at 192.168.0.101 wants to communicate with another device, using the subnet mask it knows that anything with the IP address 192.168.0.xxx is on the same local network.
Another way to express this is with a network ID, which is just the network portion of the IP address. So the network ID of the address 192.168.0.101 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 is 192.168.0.0.
And it's the same for the other devices on the local network (192.168.0.102, 192.168.0.103, and so on).
What Does CIDR Mean and What is CIDR Notation? CIDR stands for Classless Inter-Domain Routing, and is used in IPv4, and more recently, IPv6 routing.
1920px-IP_Address_Match.svg Source: Classless Inter-Domain Routing CIDR was introduced in 1993 as a way to slow the usage of IPv4 addresses, which were quickly being exhausted under the older Classful IP addressing system that the internet was first built on.
CIDR encompasses a couple of major concepts.
The first is Variable Length Submasking (VLSM), which basically allowed network engineers to create subnets within subnets. And those subnets could be different sizes, so there would be fewer unused IP addresses.
The second major concept CIDR introduced is CIDR notation.
CIDR notation is really just shorthand for the subnet mask, and represents the number of bits available to the IP address. For instance, the /24 in 192.168.0.101/24 is equivalent to the IP address 192.168.0.101 and the subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
How to Calculate CIDR Noation To figure out the CIDR notation for a given subnet mask, all you need to do is convert the subnet mask into binary, then count the number of ones or "on" digits. For example:
TYPE DECIMAL BINARY Subnet mask 255.255.255.0 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 Because there's three octets of ones, there are 24 "on" bits meaning that the CIDR notation is /24.
You can write it either way, but I'm sure you'll agree that /24 is a whole lot easier to write than 255.255.255.0.
This is usually done with an IP address, so let's take a look at the same subnet mask with an IP address:
TYPE DECIMAL BINARY IP address 192.168.0.101 11000000.10101000.00000000.01100101 Subnet mask 255.255.255.0 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 The first three octets of the subnet mask are all "on" bits, so that means that the same three octets in the IP address are all network bits.
Let's take a look at the last forth octet in a bit more detail:
TYPE DECIMAL BINARY IP address 101 01100101 Subnet mask 0 00000000 In this case, because all the bits for this octet in the subnet mask are "off", we can be certain that all of the corresponding bits for this octet in the IP address are part of the host.
When you write CIDR notation it's usually done with the network ID. So the CIDR notation of the IP address 192.168.0.101 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 is 192.168.0.0/24.
To see more examples of how to calculate the CIDR notation and network ID for a given IP address and subnet mask, check out this video:
Classful IP Addressing Now that we've gone over some basic examples of subnetting and CIDR, let's zoom out and look at what's known as Classful IP addressing.
Back before subnetting was developed, all IP addresses fell into a particular class:
subnetting Source: Subnetting for dummies Note that there are class D and E IP addresses, but we'll go into these in more detail a bit later.
Classful IP addresses gave network engineers a way to provide different organizations with a range of valid IP addresses.
There were a lot of issues with this approach that eventually lead to subnetting. But before we get into those, let's take a closer look at the different classes.
Class A IP Addresses For Class A IP addresses, the first octet (8 bits / 1 byte) represent the network ID, and the remaining three octets (24 bits / 3 bytes) are the host ID.
Class A IP addresses range from 1.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255, with a default mask of 255.0.0.0 (or /8 in CIDR).
This means that Class A addressing can have a total of 128 (27) networks and 16,777,214 (224-2) usable addresses per network.
Also, note that the range 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 within the Class A range is reserved for host loopback address (see RFC5735).
Class B IP Addresses For Class B IP addresses, the first two octets (16 bits / 2 bytes) represent the network ID and the remaining two octets (16 bits / 2 bytes) are the host ID.
Class B IP addresses range from 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255, with a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 (or /16 in CIDR).
Class B addressing can have 16,384 (214) network addresses and 65,534 (216) usable addresses per network.
Class C IP Addresses For Class C IP addresses, the first three octets (24 bits / 3 bytes) represent the network ID and the last octet (8 bits / 1 bytes) is the host ID.
Class C IP Addresses range from 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255, with a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (or /24 in CIDR).
Class C translates to 2,097,152 (221) networks and 254 (28-2) usable addresses per network.
Class D and Class E IP Addresses The last two classes are Class D and Class E.
Class D IP addresses are reserved for multicasts. They occupy the range from 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
Class E IP addresses are experimental, and are anything over 240.0.0.0.
The Issue with Classful IP Addresses The main issue with classful IP addresses is that it wasn't efficient, and could lead to a lot of wasted IP addresses.
For example, imagine that you're part of a large organization back then. Your company has 1,000 employees, meaning that it would fall into class B.
But if you look above, you'll see that a class B network can support up to 65,534 usable addresses. That's way more than your organization would likely need, even if each employee had multiple devices with a unique address.
And there was no way your organization could fall back to class C – there just wouldn't be enough usable IP addresses.
So while classful IP addresses were used around the time IPv4 addresses became widespread, it quickly became clear that a better system would be necessary to ensure we wouldn't use up all of the ~4.2 billion usable addresses.
Classful IP addresses haven't been used since they were replaced by CIDR in 1993, and are mostly studied to understand early internet architecture, and why subnetting is important.
ბ. ₽჻ Åsternak.com = мосიкаЛ гет ©A
When I 💽 code speiskit relative egzoplanets visualisation I get 🐐 in code such codé i https://www.asterank.com/exoplanets betaversion med georgiska tider i main.js epoque: if(obj['p_temp']<323.16&&obj['p_temp']>273.16&&obj['p_radius']<100){heatcolor=new THREE.Color(0x00ff00);}
it means to show egzoplanets with 🌏 planet🌡 temp range <323.16&&obj['p_temp']>273 wich means 0° to 50° range 🌏 planet with / baraxel, none | straightbaraxel. $Å, jag bestämm att så kallad ♨ 🧓 age proportial to atmospherik 🌡 temperature & pressure atmosphérique ... მააშ, gau ⬅👈!
The Celcius scale was originally based on the freezing and boiling points of water, so 0 °C was chosen as the freezing point until 1954. But now, the size of one degree on both Celcius and Kelvin scales is defined as 1/273.16 of the difference between absolute zero and the triple point of VSMOW (for various reasons relating to the actual measurement), but the 0 point of the Celcius scale was left as the freezing point of water which means that even though both scales are defined at 0 K and 273.16 K (the triple point), the Celcius scale still starts at the freezing point and 0.01 °C was defined as the triple point of VSMOW, which means 0 °C = 273.15 K.
Absolute zero is the coldest possible thermodynamic temperature, 0 K. The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid, liquid, and gas phases can exist in a stable equilibrium. If you look at the phase diagram below, it's the point at which the solid, liquid, and gas regions all meet. For water, the temperature of the triple point (273.16 K) is remarkably close to its freezing point at atmospheric pressure (273.15 K). Because 0 °C was originally defined as the freezing point of water, instead of changing the zero point when they redefined the scale based on absolute zero and the triple point, they decided to define the triple point as 0.01 °C.
We add 273.15 to °C to get kelvins because that's the difference between 0 K and 0 °C. We don't add 273.16 because the triple point is not 0 °C.
TO view µBA℞ conventer to ₽A$©AL click on image below 🥕 https://www.thermopedia.com/content/1150/
https://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/fr-FR/pressure/23-1/millibar-pascal/
Just after we 🚡can vi 🚠 kann snacka om ||||||| ///////\\\\ sequenscing ☵ etc 👽 mm 🤶 libes zuschauer von SCH [$©H] ДСН ✡ Дис💿ней хей вт🦇 დისჰეი, ცნობილი დინეი ... ЭДеп Отмеченное как eden: Tack till bA℞kusina för d'BÅRG🍔aniserad skjuss med mediciჼ cortégé; men jag gärna se henne här; för att bli säckrad om 🕉 hennes demokratiska nivån, för att man tycker tusen sake 🍶 när hans kusina skydder vaktemanner; vilka typ öppnar dörr ett par gånger per år ått henne! Och det är viktigt att veta vad det gäller då! Tack!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_barcoding

gеном человека полностью расшифрован? а вы всё медлите?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VnyhMLbwdRE
моя работа хоть как убиенного хвастаться вами ... по грузинский трабахо_б, и мне льстит что у я получаеться вы, все такие расспрекрасные но в нектрых случиях вероятно и гвазулия рпиглашённо примыкал к отчевшымсья бейбичка бабушка ... в послевоенном винституте врепродукции человакА ... ведь 6 поколении нужно интенсивно размножаться после войн ... хоть гипопотетичесскийх илижек полухенных кадров из космоса /// предлагаю рассмотрим щхастливые сценарии ... ведь такая дешёвая лажа что камуто нужны дешёвая рабочая сила, каторая вам только испортит, созданное веками да и вероятно и не поймёт что можно а что ниет льзя. шутка бабушка гинекологша что нектрые жекщина не ухаживают за свойми садами, что к нижним губам нужно поднести стакан сводой, чтоб распознать гап ...
авм истереп иткине данную щену сняли на мужчин, тойсть к верхнийм губам, где не требовалось вставить зиеркало миракли ...
... ну уже и так всё ... как говориться хорошему сказёру хорошые слушатели нжны ... а у меня вообше работа в бестселере или вообще в фильме быдущего АРД
АРТЗ ... как можно отказываться от диалектов физикачимия или вообще от бабушкА ? тем более обнаружив вовсе другие миры ... яяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяяя
другие методы создания имунитетов ...




