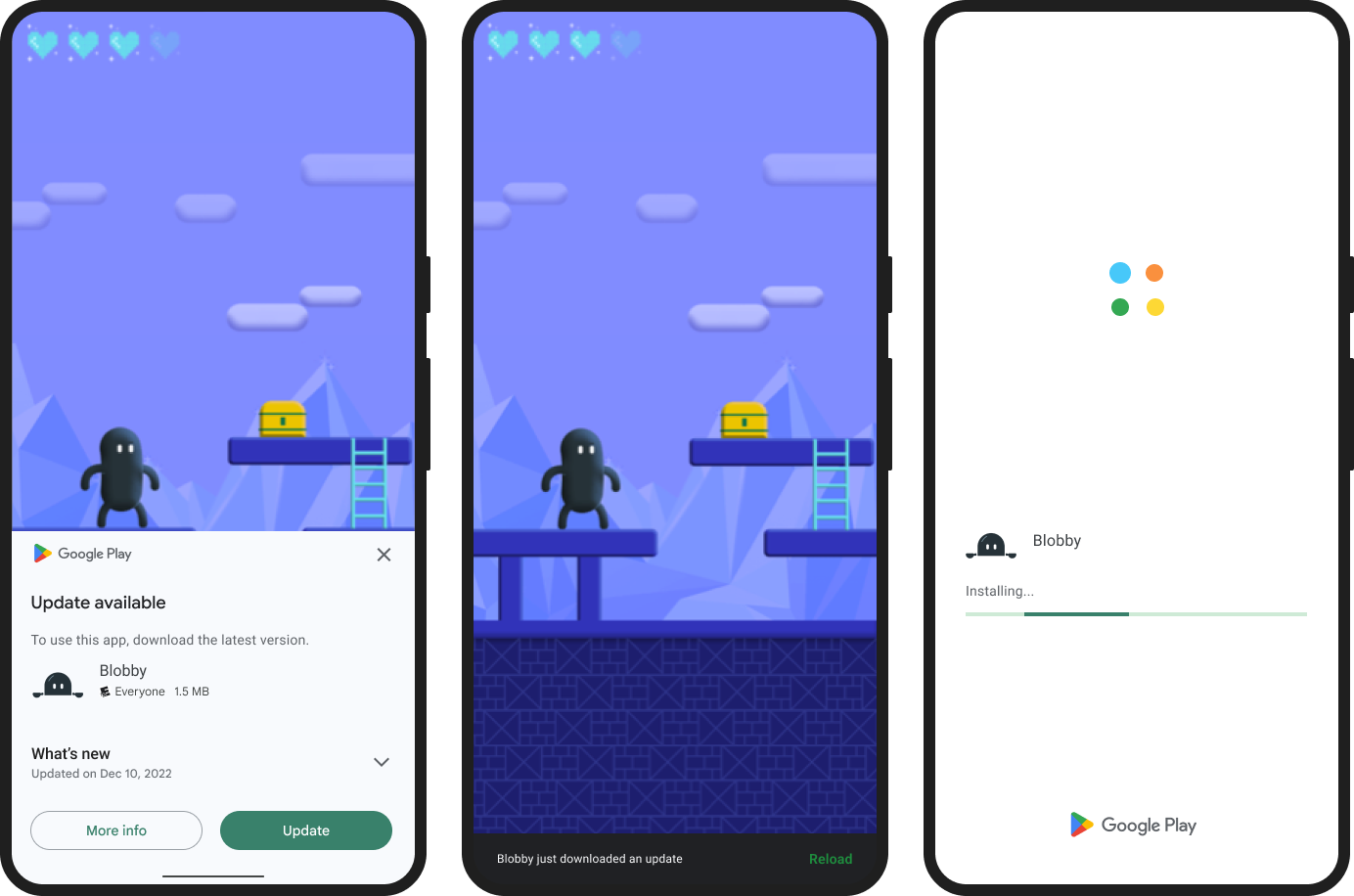
A lightweight and easy-to-use module for implementing native in-app updates for Android and iOS.
This module uses the Android native in-app updates library on Android and iTunes Search API on iOS.
On Android, it will show a native overlay like the screenshots below but on iOS it opens the app in the App Store on a modal to update the app, since iOS does not have any in-app update solution. You may want to show an alert or custom UI on iOS. See the example at the bottom.
npm install expo-in-app-updatesFor iOS, add your AppStoreID (the id in your app store link, e.g https://apps.apple.com/pl/app/example/id1234567890) in infoPlist in your app.json / app.config.js.
If your app is not available in the US, the default lookup might not find it. To fix this, you can set the AppStoreCountry to a country code where your app is available (e.g pl for Poland) in infoPlist in your app.json / app.config.js.
{
"expo": {
"ios": {
"infoPlist": {
"AppStoreID": "1234567890",
"AppStoreCountry": "pl" // Optional, only if the iTunes lookup used by this library doesn't find your app
}
}
}
}For bare React Native projects, you must ensure that you have installed and configured the
expopackage before continuing. Runnpx pod-installafter installing the npm package for iOS.
npx expo run:android | run:iosconst {
updateAvailable,
flexibleAllowed,
immediateAllowed,
storeVersion,
releaseDate,
daysSinceRelease
} = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();Checks if an app update is available. Return a promise that resolves updateAvailable and storeVersion for Android and iOS, flexibleAllowed and immediateAllowed for Android.
updateAvailable: If an update is available.flexibleAllowed: If able to start a Flexible Update (Android)immediateAllowed: If able to start an Immediate Update (Android)storeVersion: The latest app version published in the App Store / Play Store. On Android, this is theversionCodethat you defined inapp.json.releaseDate: The release date of the current version of the app (iOS)daysSinceRelease: The value of the clientVersionStalenessDays. If an update is available or in progress, this will be the number of days since the Google Play Store app on the user's device has learnt about an available update. If update is not available, or if staleness information is unavailable, this will be null. (Android)
const isUpdateStarted = await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();Starts an in-app update. Return a boolean whether the update was started successfully.
Note
If you want an Immediate Update that will cover the app with the update overlay, pass true to this function. By default, it will start a Flexible Update. More details : https://developer.android.com/guide/playcore/in-app-updates#update-flows
const isUpdateStarted = await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate(true);const isUpdateStarted = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkAndStartUpdate();Checks if an app update is available and starts the update process if necessary. Return a boolean whether the update was started successfully.
Note
If you want an Immediate Update that will cover the app with the update overlay, pass true to this function. By default, it will start a Flexible Update. More details : https://developer.android.com/guide/playcore/in-app-updates#update-flows
const isUpdateStarted = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkAndStartUpdate(true);Tip
You may want to check for updates and show an alert or custom UI on iOS. Since iOS does not have any in-app update solution, it just opens the app in the App Store on a modal to update the app. See the example below.
This example will ask the user for update the app if update available on every app startup until the user update the app.
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Alert, Platform, Text, View } from "react-native";
import * as ExpoInAppUpdates from "expo-in-app-updates";
const useInAppUpdates = () => {
useEffect(() => {
if (__DEV__ || Platform.OS === "web") return;
const checkForUpdates = async () => {
try {
if (Platform.OS === "android") {
// If you want an immediate update that will cover the app with the update overlay, set it to true.
// More details: https://developer.android.com/guide/playcore/in-app-updates#update-flows
await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkAndStartUpdate(false);
} else {
const result = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();
if (!result.updateAvailable) return;
Alert.alert(
"Update available",
"A new version of the app is available with many improvements and bug fixes. Would you like to update now?",
[
{
text: "Update",
isPreferred: true,
onPress: async () => {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();
} catch (err) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", err);
}
},
},
{ text: "Cancel" },
]
);
}
} catch (err) {
console.error("Update check failed:", err);
}
};
checkForUpdates();
}, []);
};
export default function App() {
// Use this hook in your root app or root layout component
useInAppUpdates();
return (
<View>
<Text>Native in-app updates for Android and iOS</Text>
</View>
);
}This example will ask the user for update the app if update available and if user don't update or cancel the update, then the user will not be asked again for the update until a new version published again.
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Alert, Platform } from "react-native";
import AsyncStorage from "expo-sqlite/async-storage";
import * as ExpoInAppUpdates from "expo-in-app-updates";
const useInAppUpdates = () => {
useEffect(() => {
if (__DEV__ || Platform.OS === "web") return;
const checkForUpdates = async () => {
try {
const result = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();
if (!result.updateAvailable) return;
// Get the last saved storeVersion from your local-storage (AsyncStorage/MMKV)
const savedStoreVersion = await AsyncStorage.getItem("savedStoreVersion");
// Check and return from here to prevent asking for updates again for the same storeVersion.
if (savedStoreVersion === result.storeVersion) return;
if (Platform.OS === "android") {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();
// Saving the storeVersion after checked for updates, so we can check and ignore asking for updates again for the same storeVersion
await AsyncStorage.setItem("savedStoreVersion", result.storeVersion);
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", updateErr);
}
return;
}
Alert.alert(
"Update available",
"A new version of the app is available with many improvements and bug fixes. Would you like to update now?",
[
{
text: "Update",
isPreferred: true,
onPress: async () => {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();
await AsyncStorage.setItem("savedStoreVersion", result.storeVersion);
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", updateErr);
}
},
},
{
text: "Cancel",
onPress: async () => {
try {
// Saving the storeVersion after checked for updates, so we can check and ignore asking for updates again for the same storeVersion
await AsyncStorage.setItem("savedStoreVersion", result.storeVersion);
} catch (storageErr) {
console.error("Failed to save version:", storageErr);
}
},
},
]
);
} catch (err) {
console.error("Update check failed:", err);
}
};
checkForUpdates();
}, []);
};This example checks and prevents asking for updates for 2 days after release of the app.
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Alert, Platform } from "react-native";
import * as ExpoInAppUpdates from "expo-in-app-updates";
function getDiffInDays(date) {
const diffInMs = Math.abs(new Date() - new Date(date)); // Calculate difference in ms
return diffInMs / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24); // Convert ms to days
}
const useInAppUpdates = () => {
useEffect(() => {
if (__DEV__ || Platform.OS === "web") return;
const checkForUpdates = async () => {
try {
const result = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();
if (!result.updateAvailable) return;
// Check and prevent asking for updates for 2 days after release
if (Platform.OS === "android" && ((result.daysSinceRelease??0) >= 2)) {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", updateErr);
}
return;
}
// Check and prevent asking for updates for 2 days after release
if (result.releaseDate && getDiffInDays(result.releaseDate) >= 2) {
Alert.alert(
"Update available",
"A new version of the app is available with many improvements and bug fixes. Would you like to update now?",
[
{
text: "Update",
isPreferred: true,
onPress: async () => {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate();
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", updateErr);
}
},
},
{ text: "Cancel" },
]
);
}
} catch (err) {
console.error("Update check failed:", err);
}
};
checkForUpdates();
}, []);
};You can listen to various events during the update process to provide a better user experience.
updateStart: Triggered when an update process has startedupdateDownloaded: Triggered when an update has been downloaded and is ready to installupdateCancelled: Triggered when the user cancels the update processupdateCompleted: Triggered when an update has been successfully installed
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Alert, Platform, Text, View, StyleSheet } from "react-native";
import * as ExpoInAppUpdates from "expo-in-app-updates";
const UpdateStatusScreen = () => {
const [isUpdating, setIsUpdating] = useState(false);
const [updateMessage, setUpdateMessage] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
if (__DEV__ || Platform.OS === "web") return;
// Set up event listeners - each returns a cleanup function
const startUnsubscribe = ExpoInAppUpdates.addUpdateListener(
"updateStart",
(event) => {
setIsUpdating(true);
setUpdateMessage(`Update process started (${event.updateType || "standard"})`);
}
);
const downloadedUnsubscribe = ExpoInAppUpdates.addUpdateListener(
"updateDownloaded",
() => {
setUpdateMessage("Update downloaded, ready to install!");
}
);
const cancelledUnsubscribe = ExpoInAppUpdates.addUpdateListener(
"updateCancelled",
(event) => {
setIsUpdating(false);
setUpdateMessage(`Update cancelled${event.reason ? ": " + event.reason : ""}`);
}
);
const completedUnsubscribe = ExpoInAppUpdates.addUpdateListener(
"updateCompleted",
() => {
setIsUpdating(false);
setUpdateMessage("Update completed!");
}
);
// Check for updates
const checkForUpdates = async () => {
try {
const result = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();
if (result.updateAvailable) {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate(true); // Start immediate update
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Error starting update:", updateErr);
}
}
} catch (checkErr) {
console.error("Error checking for updates:", checkErr);
}
};
checkForUpdates();
// Cleanup listeners when component unmounts
return () => {
startUnsubscribe();
downloadedUnsubscribe();
cancelledUnsubscribe();
completedUnsubscribe();
};
}, []);
if (!isUpdating && !updateMessage) {
return null;
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>App Update</Text>
<Text style={styles.message}>{updateMessage}</Text>
</View>
);
};Note
Events are primarily useful on Android, where the update flow can be tracked. On iOS, since updates happen through the App Store, fewer events are supported (mainly updateStart and updateCancelled).
If you need to enforce critical updates and prevent users from using the app until they update, you can implement a blocking UI when updates are cancelled. This is useful for security fixes or breaking API changes.
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, Button, Platform, BackHandler } from 'react-native';
import * as ExpoInAppUpdates from 'expo-in-app-updates';
// App component with forced update mechanism
export default function App() {
const [showUpdateBlocker, setShowUpdateBlocker] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
checkForMandatoryUpdate();
// Listen for update cancellation
const unsubscribeCancelled = ExpoInAppUpdates.addUpdateListener(
'updateCancelled',
() => {
setShowUpdateBlocker(true);
}
);
// Prevent back button from dismissing the blocker screen on Android
const backHandler = BackHandler.addEventListener('hardwareBackPress', () => {
return showUpdateBlocker; // True prevents default behavior
});
// Cleanup
return () => {
unsubscribeCancelled();
backHandler.remove();
};
}, [showUpdateBlocker]);
const checkForMandatoryUpdate = async () => {
if (__DEV__ || Platform.OS === "web") return;
try {
const result = await ExpoInAppUpdates.checkForUpdate();
if (result.updateAvailable) {
// Use immediate update on Android for more enforcement
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate(true);
} catch (updateErr) {
console.error("Failed to start update:", updateErr);
// Even if update fails, we should still block the app to force the user to update
setShowUpdateBlocker(true);
}
}
} catch (checkErr) {
console.error("Update check failed:", checkErr);
}
};
const retryUpdate = async () => {
try {
await ExpoInAppUpdates.startUpdate(Platform.OS === 'android');
setError(null); // Clear any previous errors on retry
} catch (retryErr) {
console.error("Retry update failed:", retryErr);
}
};
// Block access if update was cancelled
if (showUpdateBlocker) {
return (
<View style={styles.blockingContainer}>
<Text style={styles.title}>Update Required</Text>
<Text style={styles.message}>
A critical update is required to continue using the app.
Please update to the latest version to access new features and fixes.
</Text>
<Button title="Update Now" onPress={retryUpdate} />
</View>
);
}
// Your actual app content
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>Welcome to the app!</Text>
{/* Your app content goes here */}
</View>
);
}This example:
- Detects when a user cancels an update using the event system
- Shows a blocking screen that prevents app usage
- Disables the Android back button from dismissing the blocker
- Provides a simple button to retry the update
- Uses immediate updates on Android for stronger enforcement
You can enhance this solution by storing version requirements in your backend to control which app versions must be updated.
Use internal app sharing of Play Console to Test in-app updates
To test in-app updates on iOS:
- First publish your app to App Store at least once. Then make sure you have set the correct
AppStoreIDin yourapp.json/app.config.js. - Create a Development/Production/TestFlight build with a lower version number than your App Store version
- Install the build on your device
- Run the app and the update check should detect the newer App Store version
Note
The iTunes Search API used for version checking may have some delay in reflecting the latest App Store version. It's recommended to wait a few minutes after publishing a new version before testing.
See CHANGELOG.md for a list of changes in each release.