E-commerce platforms like Amazon, Shopify, and BigCommerce rely on APIs to handle user authentication, product management, and order processing. This guide demonstrates how to build a real-world RESTful API for T2S Services using Node.js, Express, and MongoDB. The API will support user registration, product catalog management, and secure order processing.
- Users can register and log in securely with hashed passwords and JWT authentication.
- Admins can manage products, ensuring only authorized users can create or modify items.
- Retrieve a list of products from the database.
- Admins can add, update, and delete products dynamically.
- Users can place orders for available products.
- The API automatically deducts stock after a successful purchase.
- Run the following in your terminal:
mkdir t2s-ecommerce-api
cd t2s-ecommerce-api
npm init -y- This will create a package.json file.
npm install express mongoose bcryptjs jsonwebtoken dotenv cors body-parser- express: Web framework for APIs.
- mongoose: MongoDB ODM for database operations.
- bcryptjs: Password hashing for authentication.
- jsonwebtoken: Secure authentication with JWT.
- dotenv: Environment variables.
- cors: Cross-Origin Resource Sharing.
- body-parser: Parse incoming JSON requests.
t2s-ecommerce-api/
│── config/
│ ├── db.js
│── models/
│ ├── Enrollment.js
│ ├── User.js
│ ├── Product.js
│ ├── Order.js
│── public/
│ ├── Emmanuel-N.JPG
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── script.js
│ ├── styles.css
│── routes/
│ ├── Enrollment.js
│ ├── userRoutes.js
│ ├── productRoutes.js
│ ├── orderRoutes.js
│── middleware/
│ ├── authMiddleware.js
│── screenshots/
│── app.js
│── .env
│── package.json
│── README.md
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
await mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
});
console.log("MongoDB Connected");
} catch (error) {
console.error("MongoDB Connection Error:", error);
process.exit(1);
}
};
module.exports = connectDB;const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const UserSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
username: { type: String, required: true, unique: true },
password: { type: String, required: true },
isAdmin: { type: Boolean, default: false }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("User", UserSchema);const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const ProductSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
description: { type: String, required: true },
price: { type: Number, required: true },
stock: { type: Number, required: true }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Product", ProductSchema);
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const OrderSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
userId: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "User", required: true },
productId: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "Product", required: true },
quantity: { type: Number, required: true },
totalPrice: { type: Number, required: true },
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Order", OrderSchema);const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const EnrollmentSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
firstName: { type: String, required: true },
lastName: { type: String, required: true },
phone: { type: String, required: true },
email: { type: String, required: true, unique: true },
course: { type: String, required: true }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Enrollment", EnrollmentSchema);const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const authMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
const token = req.header("Authorization")?.split(" ")[1];
if (!token) return res.status(401).json({ message: "Unauthorized" });
try {
const decoded = jwt.verify(token, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
req.user = decoded;
next();
} catch (error) {
res.status(401).json({ message: "Invalid token" });
}
};
module.exports = authMiddleware;const express = require("express");
const bcrypt = require("bcryptjs");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const User = require("../models/User");
const router = express.Router();
router.post("/register", async (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(password, 10);
const newUser = new User({ username, password: hashedPassword });
await newUser.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "User created successfully" });
});
router.post("/login", async (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
const user = await User.findOne({ username });
if (!user || !(await bcrypt.compare(password, user.password))) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: "Invalid credentials" });
}
const token = jwt.sign({ id: user._id, isAdmin: user.isAdmin }, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: "1h" });
res.json({ token });
});
module.exports = router;const express = require("express");
const Product = require("../models/Product");
const authMiddleware = require("../middleware/authMiddleware");
const router = express.Router();
router.get("/", async (req, res) => {
const products = await Product.find();
res.json(products);
});
router.post("/", authMiddleware, async (req, res) => {
const newProduct = new Product(req.body);
await newProduct.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "Product added successfully" });
});
module.exports = router;const express = require("express");
const Order = require("../models/Order");
const Product = require("../models/Product");
const authMiddleware = require("../middleware/authMiddleware");
const router = express.Router();
router.post("/", authMiddleware, async (req, res) => {
const { productId, quantity } = req.body;
const product = await Product.findById(productId);
if (!product || product.stock < quantity) {
return res.status(400).json({ message: "Not enough stock" });
}
const totalPrice = product.price * quantity;
const newOrder = new Order({ userId: req.user.id, productId, quantity, totalPrice });
product.stock -= quantity;
await product.save();
await newOrder.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "Order placed successfully" });
});
module.exports = router;const express = require("express");
const Enrollment = require("../models/Enrollment");
const router = express.Router();
// POST route to handle enrollments
router.post("/enroll", async (req, res) => {
try {
console.log("Incoming Request Data:", req.body); // Log the received data
const { firstName, lastName, phone, email, course } = req.body;
// Check if all fields are provided
if (!firstName || !lastName || !phone || !email || !course) {
return res.status(400).json({ message: "All fields are required." });
}
// Save to database
const newEnrollment = new Enrollment({ firstName, lastName, phone, email, course });
await newEnrollment.save();
console.log("User Enrolled Successfully:", newEnrollment);
res.status(201).json({ message: "Enrollment successful!" });
} catch (error) {
console.error("❌ Error enrolling user:", error);
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal Server Error", error: error.message });
}
});
module.exports = router;require("dotenv").config();
const express = require("express");
const connectDB = require("./config/db");
const userRoutes = require("./routes/userRoutes");
const productRoutes = require("./routes/productRoutes");
const orderRoutes = require("./routes/orderRoutes");
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
connectDB();
app.use("/api/users", userRoutes);
app.use("/api/products", productRoutes);
app.use("/api/orders", orderRoutes);
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Welcome to T2S E-Commerce API");
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5050;
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server running on http://127.0.0.1:${PORT}`));-
If running MongoDB locally, do the following:
- Create the .env if it does not exist.
ls -la # To verify if the .env exists.
touch .env # To create the .env file- Add the following content to the **.env** file:
# Database Connection
MONGO_URI=mongodb://localhost:27017/t2s-ecommerce
# Authentication & Security
JWT_SECRET=yourJWTsecret-2025
# Server Configuration
PORT=5050
# CORS Setup (Optional)
CORS_ORIGIN=*
# Debugging & Logging
NODE_ENV=development
- A little different from what you see on the screenshot below. But, basically, you need to determine the values for MONGO_URI, JWT_SECRET and PORT.

npm install express # To install Express
npm list express # To verify Express- Delete node_modules and Reinstall
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
npm install- Now go to Step 9.
1. Start MongoDB (if using local setup)
- Install MongoDB
# For macOS (Using Homebrew)
brew tap mongodb/brew
brew install mongodb-community@7.0
# After installation, start MongoDB
brew services start mongodb-community@7.0
# For Ubuntu/Linux
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y mongodb
sudo systemctl start mongodb
sudo systemctl enable mongodb
# For Windows
## -> 1. Download MongoDB Community Edition from MongoDB Download Center.
## -> 2.Install MongoDB and make sure C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\7.0\bin is added to the system PATH.
## -> 3.Start MongoDB:
# Start mongoDB
mongod
# Verify MongoDB is Running
ps aux | grep mongod
#Or, use "mongo" command** 2. Run the API**
node app.js- API is live at: http://127.0.0.1:5050/
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5050/api/enroll \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"firstName":"John", "lastName":"Doe", "phone":"1234567890", "email":"john@example.com", "course":"DevOps"}'- "firstName":"John"
- "lastName":"Doe"
- "phone":"1234567890"
- "email":"john@example.com"
- "course":"DevOps"
{
"message": "Enrollment successful!"
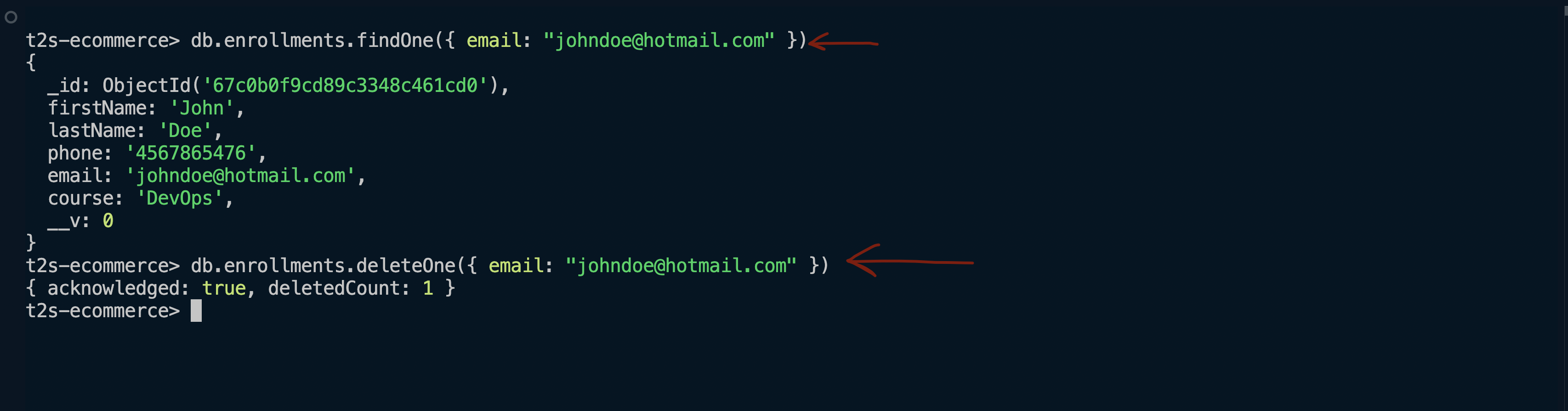
}db.enrollments.find().pretty()# Remove Unnecessary Files
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
# Ensure .gitignore is Set Up
ls -a | grep .gitignore # To check if .gitignore exists
# If missing, create it
touch .gitignore
# Add the following content:
node_modules/
.env
.DS_Store
package-lock.json
screenshots/
# Remove Local MongoDB Data (If Desired)
mongsh
use t2s-ecommerce
db.dropDatabase() # Deletes all data
exit
# Reset Git History (If Necessary)
git rm -rf --cached .
git add .
git commit -m "Cleaned up sensitive files and directories"
# Reinstall Dependencies
npm install
# Push Only the Core Components of the Infrastructure
git init
git add .
git commit -m "Pushing updated scripts for the Express API with MongoDB"
git branch -M main
git remote add origin https://github.com/Here2ServeU/api-expressJS-projects.git # If necessary
git push -u origin main This T2S Services E-commerce API provides a scalable and secure foundation for an online store, handling essential functionalities like user authentication, product management, and order processing. Future enhancements could include payment gateway integration (e.g., Stripe, PayPal), Dockerization, and deployment on AWS for high availability.