This project uses an LSTM-based deep learning model to detect fraudulent job postings with an accuracy of 98%. The solution involves extensive data preprocessing (text cleaning, tokenization, and padding), addressing class imbalance using SMOTE, and training an LSTM network to classify postings as either fraudulent or legitimate. The final model is deployed as a Flask web application and is also converted to TensorFlow Lite for edge deployment.
- Introduction
- Data Preprocessing
- Model Training
- Evaluation
- Deployment
- Technologies Used
- Folder Structure
- Installation Steps
- Conclusion
- Contributor
- License
In an era of increasing online job frauds, this project provides a deep learning-based solution to detect fraudulent job postings. By leveraging deep learning techniques and advanced data preprocessing methods, the system aims to help job seekers avoid scams and employers maintain credibility.
- Text Cleaning: Removing URLs, non-alphabetic characters, and converting text to lowercase.
- Tokenization: Converting job posting text into sequences of word indices.
- Padding: Standardizing sequence lengths to ensure uniform input.
- SMOTE: Addressing class imbalance by generating synthetic samples for the minority class.
Before training the model, an in-depth exploratory data analysis was conducted to understand the dataset and identify patterns, trends, and potential issues. Key steps included:
- Data Overview: Analyzing the structure of the dataset, including the number of features, rows, and data types.
- Class Distribution: Visualizing the distribution of fraudulent vs. legitimate job postings to identify class imbalance.
- Text Analysis: Examining the most frequent words, bigrams, and trigrams in fraudulent and legitimate postings.
- Missing Values: Identifying and handling missing or incomplete data.
- Feature Correlation: Exploring relationships between numerical features (if any) and the target variable.
Visualizations such as bar plots and more were used to gain insights into the data. This step was crucial for informing the preprocessing and modeling strategies.
An LSTM-based model is built with the following architecture:
- Embedding Layer: Converts text into dense vector representations.
- LSTM Layer: Captures sequential dependencies in the data.
- Dense & Dropout Layers: Enhance feature extraction and reduce overfitting.
- Sigmoid Activation: Produces probabilities for binary classification.
The model is compiled with binary crossentropy loss and the Adam optimizer, and trained for several epochs to achieve optimal performance.
The trained model achieves an accuracy of 98%. Evaluation is performed using precision, recall, F1-score, and a detailed classification report, confirming the model's robustness in detecting fraudulent postings.
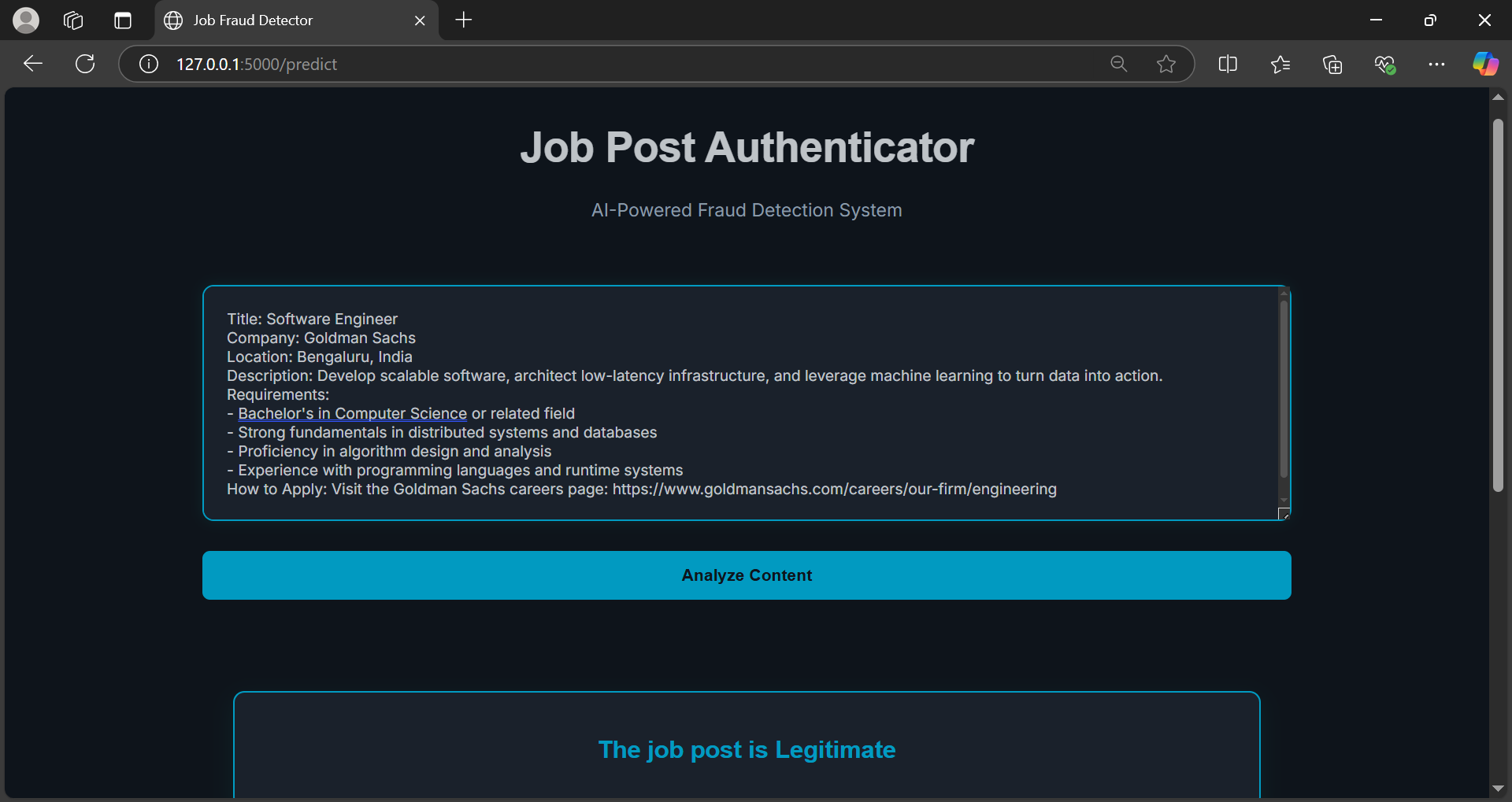
The trained model is deployed as a Flask web application, enabling real-time predictions. Additionally, the model is saved in both H5 and TFLite formats, ensuring flexibility for deployment in various environments.
├── app.py # Flask application for deployment
├── converting_model.py # Converts LSTM model to TFLite format
├── EDA_FAKE_JOB.ipynb # Jupyter Notebook for Exploratory Data Analysis
├── Model_Training.ipynb # Jupyter Notebook for Model Training
├── fake_job_lstm_model.h5 # Trained LSTM model (H5 format)
├── fake_job_lstm_model.tflite # Converted TFLite model
├── fake_job_postings.csv # Dataset of job postings
├── requirements.txt # Project dependencies
├── tokenizer.pkl # Saved tokenizer for text processing
├── README.md # Project documentation
├── assets/ # Images and screenshots
│ ├── keras.png
│ ├── matplotlib.png
│ ├── scikit-learn.png
│ ├── seaborn.png
│ ├── tensorflow.png
│ └── Working_screenshot.png # Screenshot of the working project
├── static/ # Custom styles for the web application
│ └── style.css
└── templates/ # HTML template for the Flask application
└── index.html
git clone https://github.com/38832/Fake-Job-Posting-Prediction.git
cd Fake-Job-Posting-Predictionpython -m venv venv
# Activate the virtual environment:
# On macOS/Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
# On Windows:
venv\Scripts\activatepip install -r requirements.txtpython app.pyThe Flask application will start and can be accessed at http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
This project demonstrates an effective approach to detect fraudulent job postings using deep learning. With an impressive accuracy of 98%, it provides a reliable solution to mitigate job fraud risks. The integration of advanced data preprocessing techniques, robust model training, and seamless deployment underscores its practical application in real-world scenarios.
Abutalha Shaikh - GitHub
This project does not have a license.
Feel free to contribute or reach out for any improvements!