- Communication Goal of this Document
- Safety and Security in Automotive
- Can you get sued for bad Code if Somebody gets injured?
- Formal Safety Development Standards in Automotive Software Systems
- Popular Software Development Models
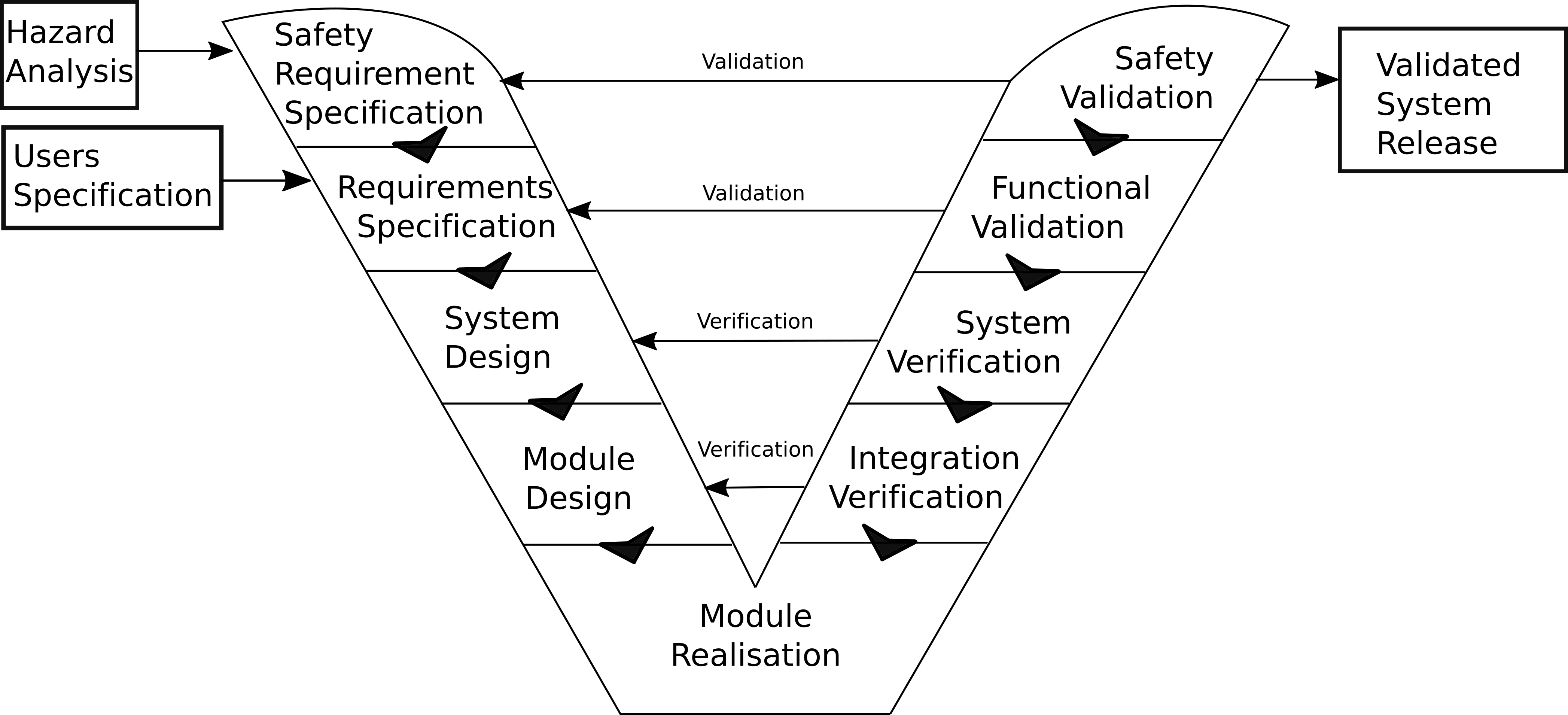
- Classical ISO26262 Development and the Conflict with Urban Autonomous Driving
- Agile System Engineering
- Operational Design Domain
- Continuous Engineering
- Separation of Concerns
- Entry point on safety related control software used in systems driving on closed and public roads
Important Note: If you need to develop a safe robotic product for the first time in your organization, you should get commercial consulting and training right from the start over your complete product life-cycle from experts like TÜV Rheinland.
Safety
The condition of being protected from or unlikely to cause danger, risk, or injury.
Safety vs. Freedom
A standing turned-off vehicle has the highest level of safety and security. Freedom is to take a risk.
Relationship between Safety and Security
is such that a weakness in security creates increased risk, which in turn creates a decrease in safety. As a result, safety and security are directly proportional, but both are inversely proportional to risk.
Safety and Security Culture
Safety and Security starts with the imagination and responsibility of every person related to the product development.
No, only if you are a original equipment manufacturer (OEM). You can not sue Linus Torvalds if your company server gets hacked, since the Linux license excludes liability. The identity selling a product with Linux is reliable for the requirements to be fulfilled.
The OEM can be sued for open source software used in its products in the first instance. To avoid this, BMW CarIT GmbH developed a open source software safety verification methods for the Linux kernel. This is also done in the ELISA project.
Autoware.Auto Apache License Version 2.0:
Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory [...] shall any Contributor be liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the Work [...] [1]
ISO 26262[1]: Addresses possible hazards caused by malfunction behavior of electrical and/or electronic in safety-related systems.
Development and integration of these systems:
- needs a safe system development process
- demonstration that all reasonable safety objectives are satisfied
Certifying your product development and supply chain by ISO26262 shows others that you are working professional. It protects you in terms of malfunction that causes damage to persons or material since you show "reasonable care".
| Waterfall | V-Model | Agile |
|---|---|---|
 |
||
| Every requirement is known right from the project start. The development order is sequential. No iteration is allowed. Good for projects where changes are very costly or impossible in between development phases. Bad for intense knowledge gathering. | It is focused on traceabilty, validation and verification in between every phase. It's segmented into chronological development phases with no iterations in between. ISO26262 demands an adaption of V-Model. | Agile Methods like Scrum or Extreme Programming are human orientated development models. Design, tests and requirements can evolve over time by iterations. This is ideal for knowledge intense development where requirements cannot be defined right from the project start with your customer. |
The requirements for an autonomous system in urban scenarios can not be manually crafted the classical way described in ISO26262 since too many scenarios appear in an unlimited public area.
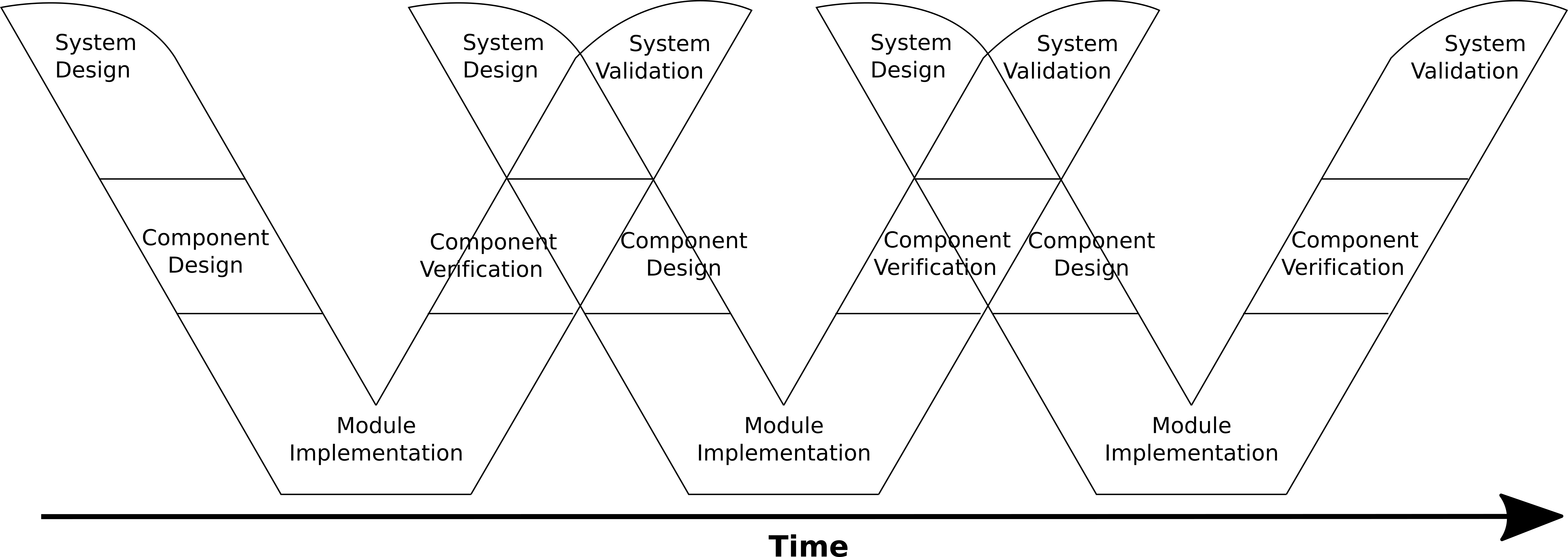
To combine the best from agile methods and traceable V-model methods the complete engineering needs to iterated in itself. This approach is called Agile System Engineering and was applied by Vector at Ford. The V-Model gets repeated until every verification and validation phase is succeeded in a traceable way.
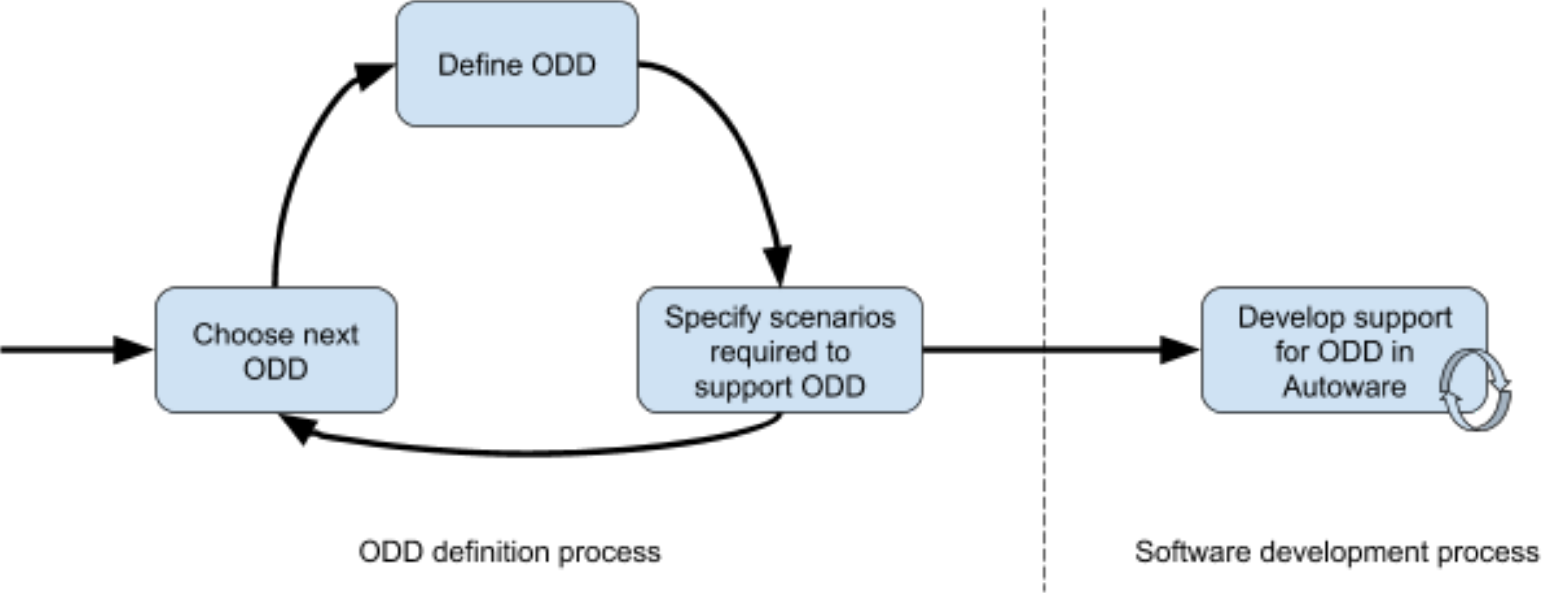
J3016 defines an Operational Design Domain (ODD) as “operating conditions under which a given driving automation system or feature thereof is specifically designed to function, including, but not limited to, environmental, geographical, and time-of-day restrictions, and/or the requisite presence or absence of certain traffic or roadway characteristics.” (LA)(3.22) ODD
An ODD may put limitations on
- the road environment
- the behavior of the equipped subject vehicle
- the state of the vehicle. [1]
This method is realized by Autoware.auto. It slices complexity and increase functionality by iterating new domains. The first domain is the Autonomous Valid Parking (AVP) based on the open source requirements provided by Parkopedia.
Is a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections such that each section addresses a separate concern. [1] [2]
A program that embodies seperation of concerns (SoC) well is called a modular program. ROS1 and ROS2 encourage SoC by the creation of nodes communicating distributed with each other over a middleware.
This allows a modular architecture design to new domains by the recombination of modules from already proven domains.
- General Design
- Develop in a Fork
- Designs and Requirements
- Validation
- Verification by Operational Design Domain
- Continuous Integration and DevOp
- Conclusion and the next Lecture
| Goal | Definition |
|---|---|
| Reliability | Executable code consistently fulfills all requirements in a predictable manner |
| Portability | Source code is portable (i.e. not compiler or linker dependent) |
| Maintainability | Source code is written in a manner that is consistent, readable, simple in design, and easy to debug |
| Testability | Source code is written to facilitate testability |
| Re-usability | The design of reusable components is encouraged. Component reuse can eliminate redundant development and test activities (i.e. reduce costs) |
| Extensibility | Requirements are expected to evolve over the life of a product. Thus, a system should be developed in an extensible manner (i.e. perturbations in requirements may be managed through local extensions rather than wholesale modifications) |
| Readability | Source code is written in a manner that is easy to read, understand, and comprehend |
Apex.ai design guidelines based on JSF-AV-rules.
Note that following the guidelines contained within this document do not guarantee the production of an error-free and safe product. However, adherence to these guidelines helps programmers produce clean designs that minimize common sources of errors. Dejan Pangercic
Autoware.Auto follows the fork-and-pull model of Git. This means that developers should make a fork of the Autoware.Auto repository, develop in branches on that fork, and then make merge requests (the GitLab term; pull requests in GitHub terminology) from that fork to the central Autoware.Auto repository. [1]
Autoware.Auto documented it's contribution workflow in detail to guide and motivate new developers to join the development.
Christopher Ho of Apex.ai gives a great inside on the development method and requirement identification for the NDT development in his blog post part 1. and part 2.
Integration is probably the hardest part of algorithm development because you need to maintain a high-level view while fixing low-level problems. Any one bug in any of your many lines of code can break the integration of your algorithm.
One of the core functions in AD is not just the algorithmic implementation itself but the integration testing infrastructure around it. More information about this mindset can be found in Test-Driven Development processes. Before creating requirements for your developments you need to find a way to test them.
Have you built it in the right way?
Verification. The evaluation of whether or not a product, service, or system complies with a regulation, requirement, specification, or imposed condition. It is often an internal process.[1]
Dynamic and static testing methods make Autoware.Auto reliable and robust, helping us to perform anomaly detection and handling that would otherwise be difficult to find. Through testing in Autoware.Auto, we can estimate the number of Heisenbugs, and find and eliminate undefined behaviour for which C and C++ languages are known. [1]
Structural code coverage is a measure of the completeness of software testing showing which areas of the source code are exercised in the application during the test. This provides a convenient way to ensure that software is not released with untested code. [2]
More information on how to write tests and measure coverage in Autoware.Auto can be found here.
Putting the pieces together is always the hard part in engineering but it is also the supreme discipline.
By replaying data into one or multiple ROS2 nodes you can create integration test in an early stage of your development. Especially with sensor data from your operational domain the complete perception can be tested based on large datasets if you have labeled ground truth.
To create closed loop integration test you will need a simulation like Ignition Robotics or LGSVL that can be integrated into continuous integration pipelines. With a pure LiDAR based perception you can therefore drive multiples scenarios automatically as a stage in the release. To achieve this you need to be able to deploy the complete software stack to the simulation. This also requires a sophisticated vehicle simulation and interfaces. In this way you can identify malfunction in an early stage of the development without failing or real hardware on your test track.
Autoware.auto provides you with guidelines on how to create integration tests.
 Two unit tests, no integtion test
Two unit tests, no integtion test
Have you built what you were planning to build based on the initial requirements?
"Validation. The assurance that a product, service, or system meets the needs of the customer and other identified stakeholders. It often involves acceptance and suitability with external customers. Contrast with verification. [1]
The Autoware Foundation has adopted an approach to technology development that focuses on a succession of achievable technological milestones. Each milestone is an Operational Design Domain, and each builds on the work of the previous milestones. [2]
In software engineering, continuous integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developers' working copies to a shared mainline several times a day. [1]
[[2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/05/Devops-toolchain.svg)DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and information-technology operations (Ops) which aims to shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality.[2]
Autoware.Auto is the most promising development in the standardization of autonomous driving technology worldwide. It creates safe methods, interfaces, terminologies, open source standards, tooling and an ecosystem from different domains.
For our development at DHL and StreetScooter Autoware.Auto is going to be a base line toolbox for safe prototyping. The AMPS system development shows, that the operational design domain is the most promising approach to deliver safe, automated systems with early business benefits for our logistic customers.
In the next lectures Katherine Scott of OpenRobotics will introduce you to the 101 of ROS2 and the tooling that is empowering Autoware.Auto.