If using notebooks, make sure to clear notebook output before committing changes to the repository. Alternatively, you can work in a branch off of main, and do a squash commit back into main when complete.
The .gitattributes file is used to assign an attribute to all notebook files, and a modification to the local .git/config file is made to call a function to clear out all notebook results before committing.
After cloning the repository for the first time, you can call
pipenv run notebooks_with_gitor, from the parent directory:
git config --local include.path ../env/.gitconfig
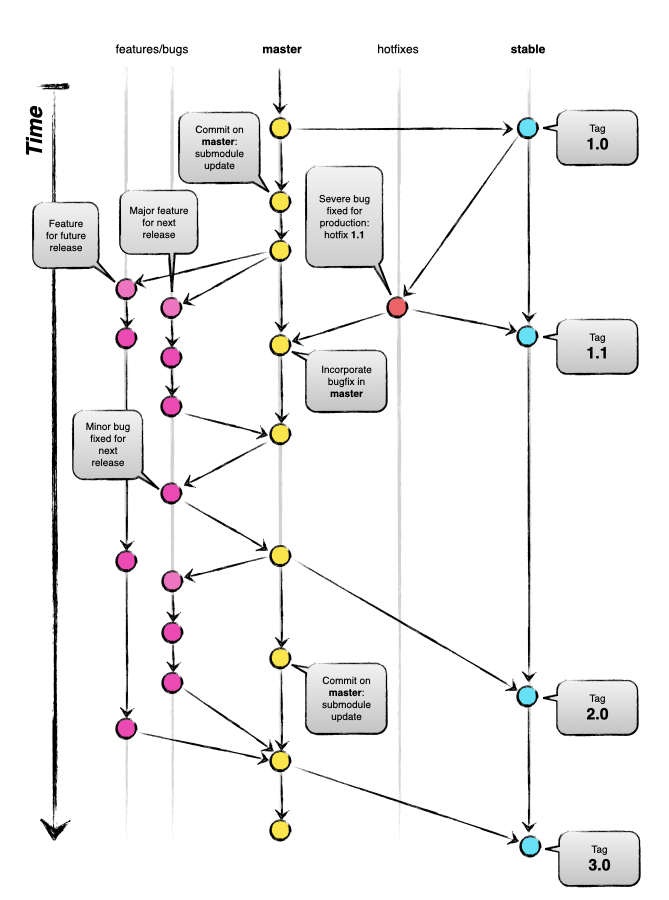
git add --renormalize .Use of branching on this project follows the methodology described in
- This branching gist by @digitalhelms
- A successful Git branching model by Vincent Driessen
There are two primary branches
mainstable
The main branch is the branch under active development with new features being added and changes being made. The stable branch contains the latest stable version of the project code. The main branch is merged into stable once all changes are ready to be applied; typically at the end of every project sprint.
Use a branch whenever working on new features, bug fixes or changes.
Used when developing general changes, improvements or new features or models.
- Branch from
main - Merge into
main - Naming:
feature-<name>(e.gfeature-LRmodel)
Similar to features, but have a specific focus on fixing errors or issues. These changes will be deployed at the next version update.
- Branch from
main - Merge into
main bug-<name>(e.gbug-slow_MLP)
Fixes that need to be deployed to production immediately. These are fixes to the stable branch.
- Branch from
stable - Merge into
stable hotfix-<name>(e.gfix-incorrect_directory)