-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7.6k
Phantom Operators
-
fromFuture( )— convert a Future into an Observable, but do not attempt to get the Future's value until a Subscriber subscribes -
forIterable( )— apply a function to the elements of an Iterable to create Observables which are then concatenated -
generate( )andgenerateAbsoluteTime( )— create an Observable that emits a sequence of items as generated by a function of your choosing
convert a Future into an Observable, but do not attempt to get the Future's value until a Subscriber subscribes
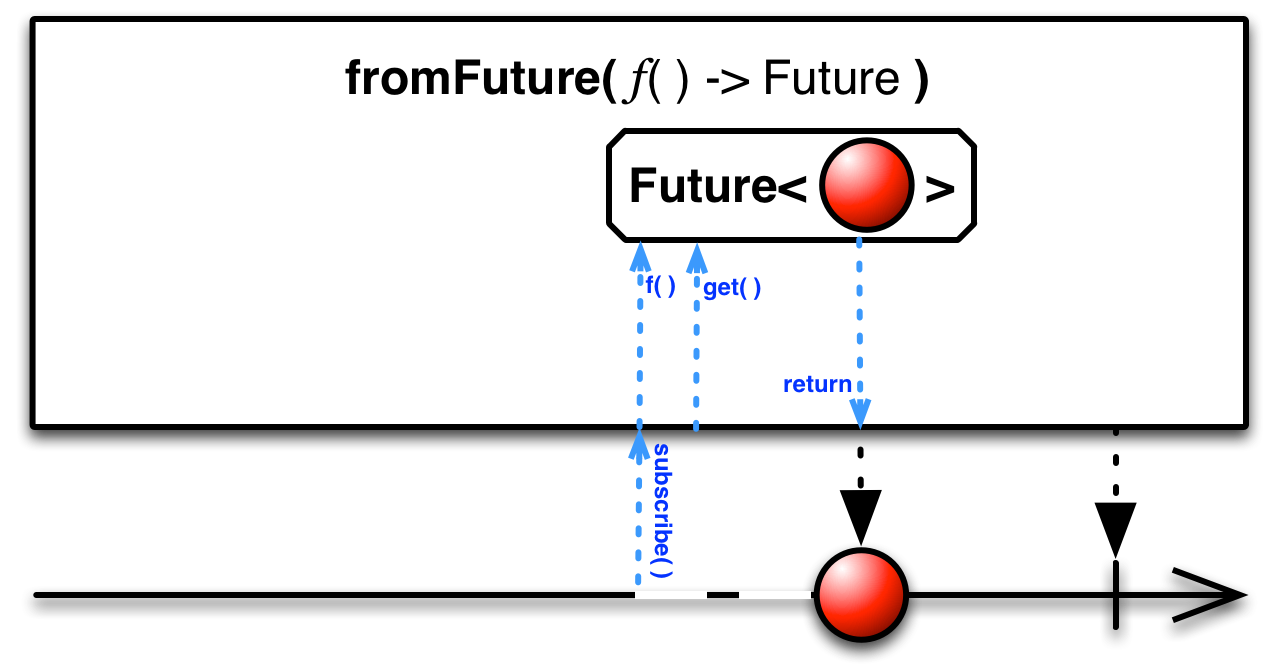
The fromFuture( ) method also converts a Future into an Observable, but it obtains this Future indirectly, by means of a function you provide. It creates the Observable immediately, but waits to call the function and to obtain the Future until a Subscriber subscribes to it.
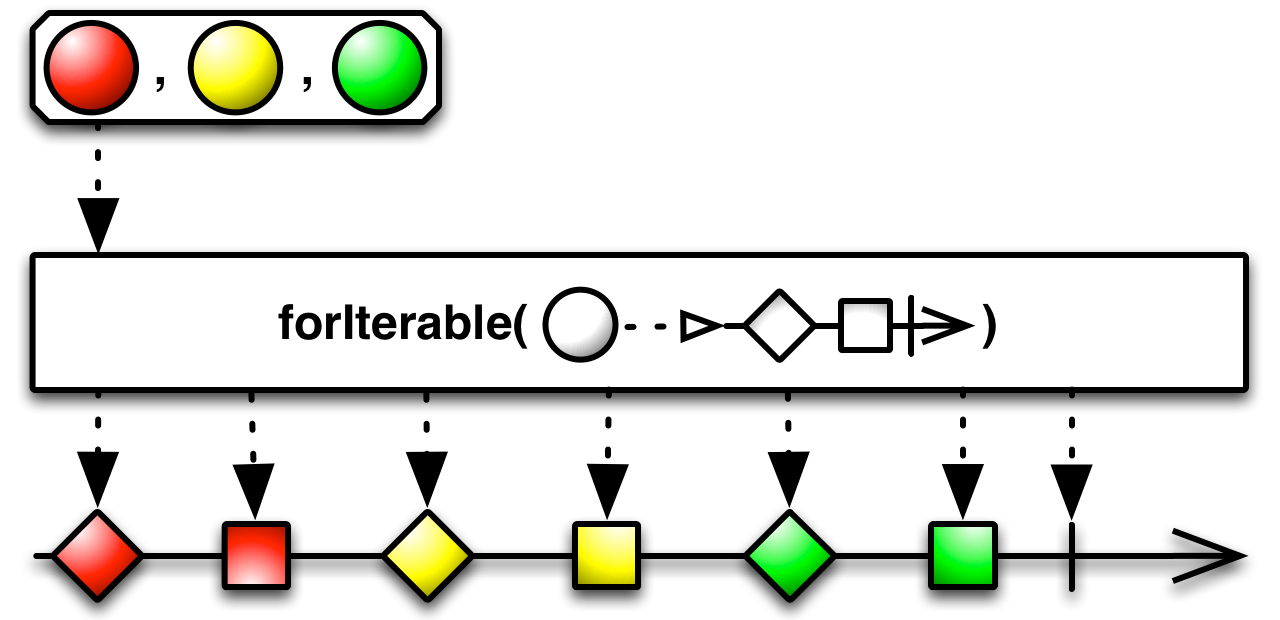
forIterable( ) is similar to from(Iterable ) but instead of the resulting Observable emitting the elements of the Iterable as its own emitted items, it applies a specified function to each of these elements to generate one Observable per element, and then concatenates the emissions of these Observables to be its own sequence of emitted items.

The basic form of generate( ) takes four parameters. These are initialState and three functions: iterate( ), condition( ), and resultSelector( ). generate( ) uses these four parameters to generate an Observable sequence, which is its return value. It does so in the following way.
generate( ) creates each emission from the sequence by applying the resultSelector( ) function to the current state and emitting the resulting item. The first state, which determines the first emitted item, is initialState. generate( ) determines each subsequent state by applying iterate( ) to the current state. Before emitting an item, generate( ) tests the result of condition( ) applied to the current state. If the result of this test is false, instead of calling resultSelector( ) and emitting the resulting value, generate( ) terminates the sequence and stops iterating the state.
There are also versions of generate( ) that allow you to do the work of generating the sequence on a particular Scheduler and that allow you to set the time interval between emissions by applying a function to the current state. The generateAbsoluteTime( ) allows you to control the time at which an item is emitted by applying a function to the state to get an absolute system clock time (rather than an interval from the previous emission).

Copyright (c) 2016-present, RxJava Contributors.
Twitter @RxJava | Gitter @RxJava