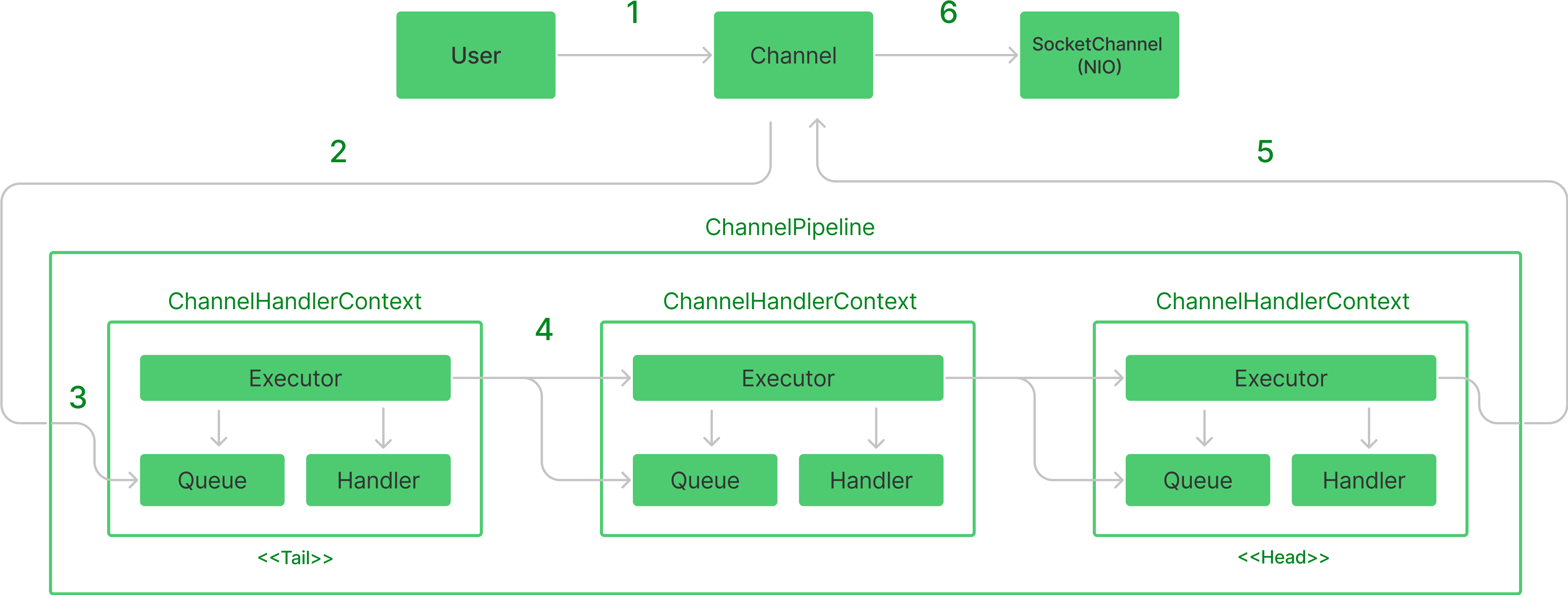
네티는 Channel을 통해서 메시지 전송을 요청한다.
Channel channel = ...
channel.writeAndFlush(message);Channel은 ChannelPipeline으로 메시지를 전달한다. ChannelPipeline은 기본적으로 TailContext, HeadContext를 가진다. (Pipeline의 시작과 끝이라고 할 수 있다.)
Tail, Head 사이에는 사용자가 등록한 ChannelHandlerContext가 체인 구조로 연결되고, 전달된 메시지가 체인을 따라 Outbound 방향으로 흘러들어간다.
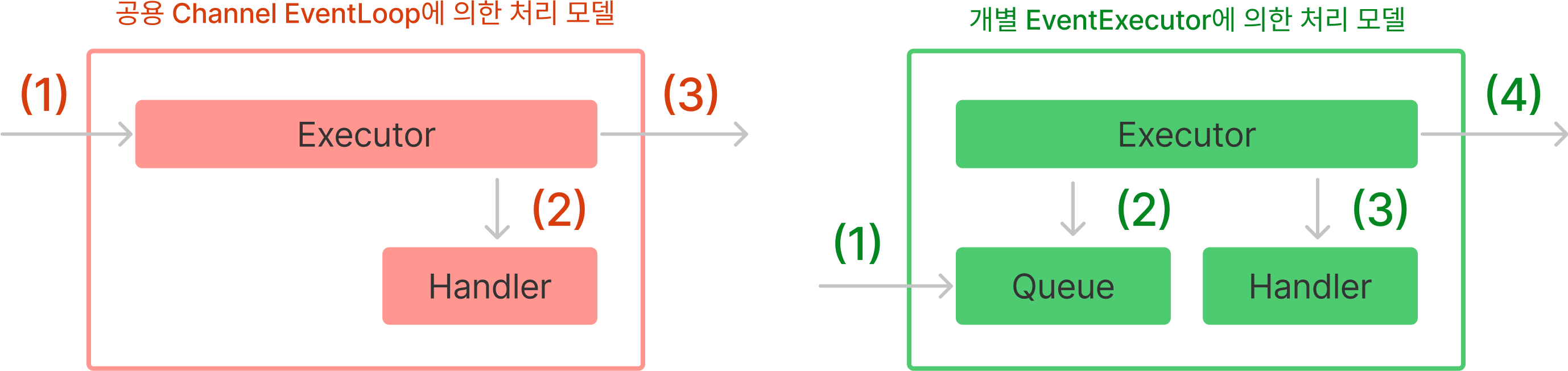
ChannelPipeline이 메시지가 각각의 핸들러를 거칠 때 마다, 핸들러에게 바인딩된 EventExecutor 스레드와 현재 메시지 전송을 요청하고 있는 스레드가 일치하는지 체크한다.
만약 서로 다른 스레드라면 메시지를 Queue에 삽입하고 그대로 실행을 반환한다. Queue에 쌓인 메시지는 이후 EventExecutor에 의해 비동기적으로 처리되게 한다. Pipeline의 첫 ChannelHandlerContext에서는 항상 요청 스레드와 EventExecutor가 다르게되고 Queue에 쌓인다.
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext ... {
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {
...
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
if (flush) {
next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);
} else {
next.invokeWrite(m, promise);
}
} else {
final WriteTask task = WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise, flush);
if (!safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m, !flush)) {
task.cancel();
}
}
...
}
}만약 사용자가 별도의 EventExecutor를 설정하지 않았다면(default) 모든 핸들러는 Channel의 EventLoop 스레드를 공유해서 사용하게 된다. 그러므로 Pipeline의 Tail 외에는 Queue에 메시지가 버퍼링되는 일이 일어나지 않는다.
반면에 사용자가 특정 Handler의 EventExecutor를 설정해주었다면, Executor가 달라지는 Handler에서는 Queue의 메시지가 버퍼링 된 후 서로 다른 EventExecutor에 의해 메시지가 비동기적으로 처리되게 된다.
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext ... {
public EventExecutor executor() {
if (executor == null) {
return channel().eventLoop();
} else {
return executor;
}
}
}Pipeline을 통과한 메시지는 다시 Channel로 전달된다.
Netty의 Channel은 내부적으로 NIO 채널을 통해 네트워크로 메시지를 전송한다.
public class NioSocketChannel ... {
protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel();
...
ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0];
int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining();
final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer);
if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) {
incompleteWrite(true);
return;
}
...
}
}